How does the thermal conductivity of a bimetallic screw affect product quality?
The Impact of a Bimetallic Screw's Thermal Conductivity on Product Quality
1. Improved Plasticizing Uniformity
By creating radial convection within the screw channel, a bimetallic screw rapidly transfers high-temperature melt toward the screw base, significantly reducing axial temperature differences and ensuring a more uniform temperature distribution throughout the entire screw channel.
Uniform temperature distribution prevents localized overheating or insufficient cooling, thereby reducing internal stress and warpage in the product.
2. Faster Heat Exchange Rate
Using bimetallic materials (such as a highly thermally conductive copper-aluminum combination) creates an efficient heat transfer channel between the screw and barrel, allowing heat to be transferred quickly and shortening the heating/cooling cycle.
Faster heat exchange increases production line productivity while reducing the effects of thermal aging on material properties.
3. Improved High-Temperature Processing Stability
Under high-temperature conditions, the bimetallic screw maintains stable thermal conductivity, enabling it to maintain a constant plasticizing temperature over long periods of continuous operation. This prevents melt viscosity fluctuations caused by temperature drift, thereby ensuring product dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
4. Reduced Energy Consumption and Maintenance Costs
Efficient heat conduction reduces heater power requirements, saving energy. Furthermore, due to fewer thermal cycles, the wear rate of the screw and barrel decreases, extending service life and indirectly improving product quality and reliability.
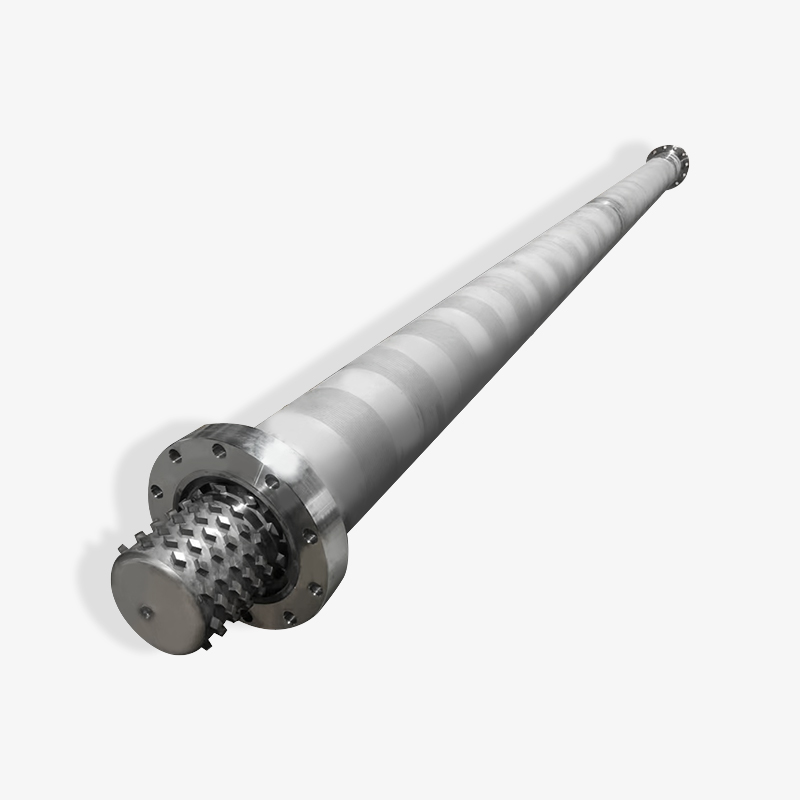
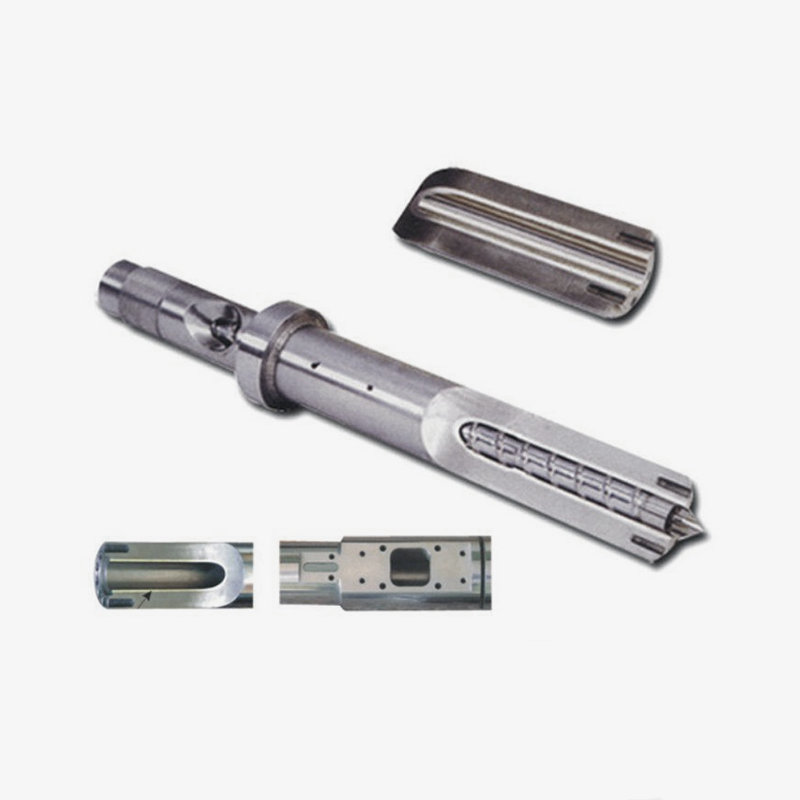
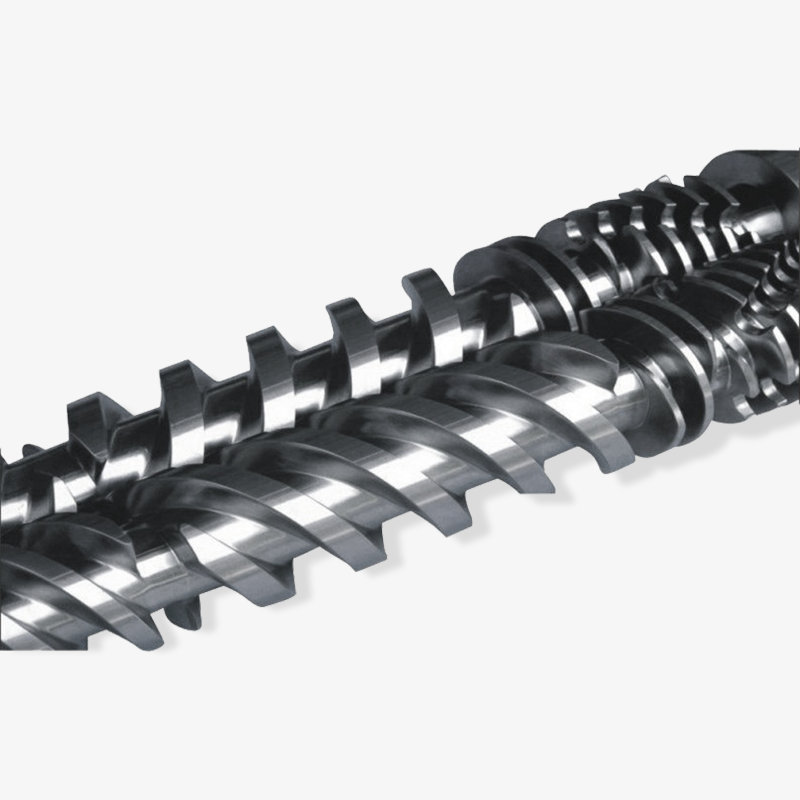
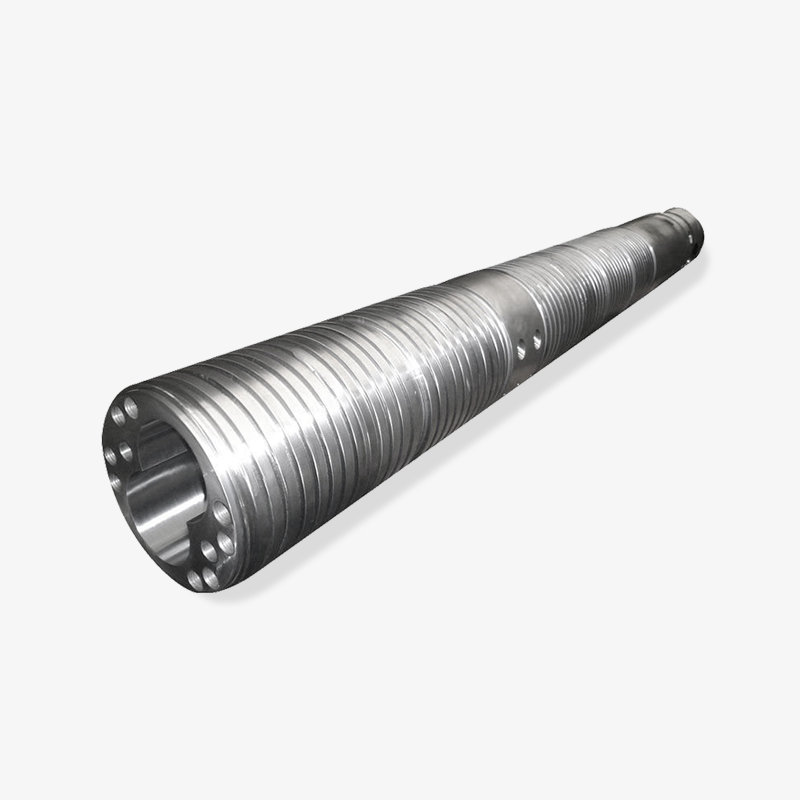
How to Determine the Quality of a Bimetallic Screw?
1. Material Hardness and Wear Resistance
The alloy layer of a high-quality bimetallic screw can reach a hardness of HRC60-70, significantly higher than that of ordinary screws, enabling long-term use in high-wear engineering plastic processing.
Hardness testing (such as the Rockwell hardness tester) is a direct means of assessing wear resistance.
2. Surface Treatment and Nitriding Layer
A screw treated with nitriding or nitriding must have a surface hardness of at least 840 HV and a nitriding layer thickness of ≥0.3 mm, significantly improving corrosion and fatigue resistance.
Inspecting the integrity and bond strength of the nitriding layer is an important indicator of surface quality.
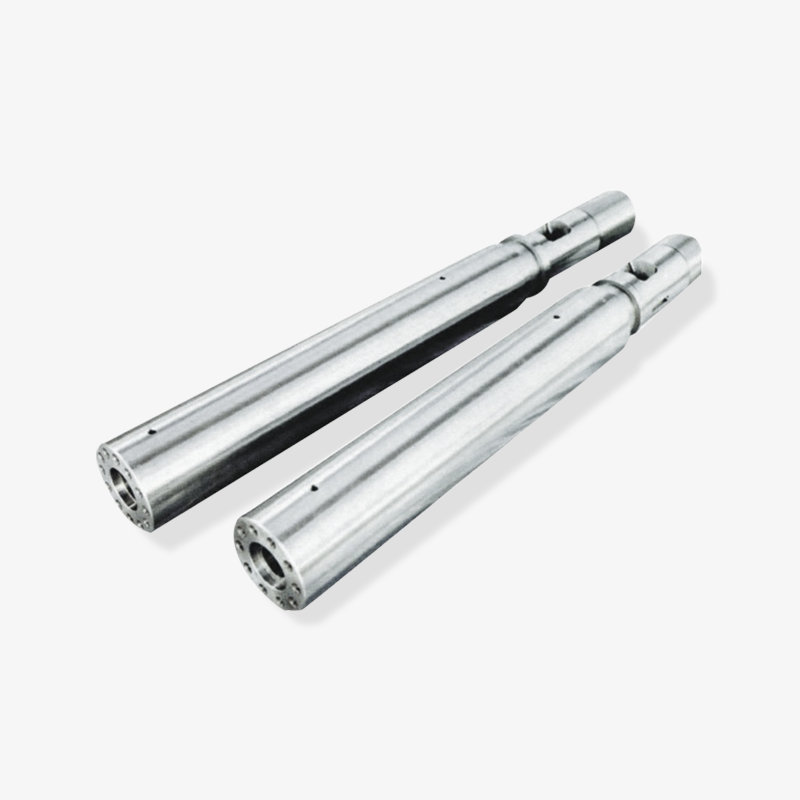
3. Alloy Composition and Corrosion Resistance
Bimetallic screws made of nickel-based alloys such as Ni-20 maintain the chemical stability of the material when processing highly corrosive plastics such as PC, PVC, and acrylic, preventing leakage or screw deformation caused by metal corrosion.
Chemical composition analysis (such as spectrometry) verifies the alloy ratio to ensure that corrosion resistance meets process requirements.
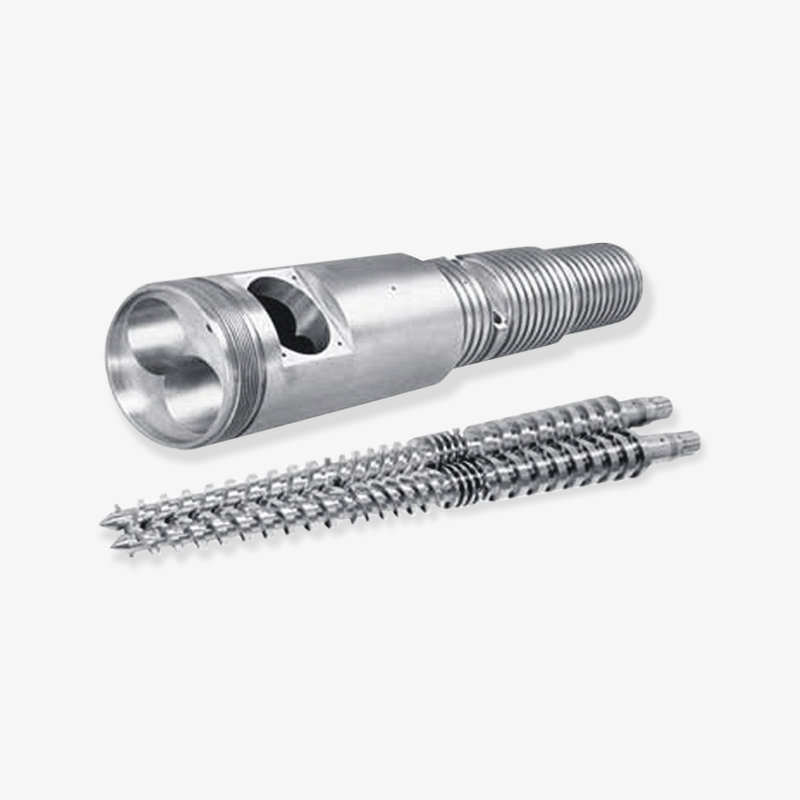
4. Manufacturing Process and Dimensional Stability
High-precision heat treatment (quenching and tempering) and precision machining ensure that the screw maintains its dimensions at high temperatures, preventing gap expansion or meshing problems caused by thermal expansion.
Zhoushan Microwave Screw Machinery Co., LTD has a professional design and production team equipped with advanced heat treatment, fine grinding, and polishing processes to meet these high-standard manufacturing requirements.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体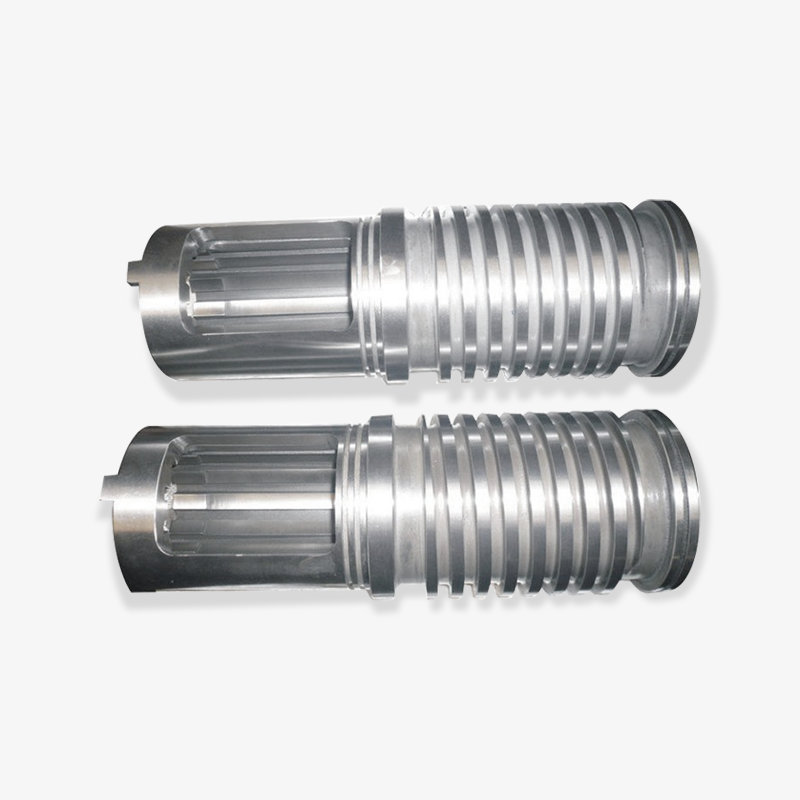










 浙公网安备33090202000520号
浙公网安备33090202000520号